Legal & Regulatory Environment of Crypto Mining by Jurisdiction (2025 Update)
Legal & Regulatory Environment of Crypto Mining by Jurisdiction continue to shape individuals and companies participating in digital assets. Around the world, nations view crypto mining in different approaches. While some embrace the innovation, others impose restrictions due to energy use, financial risks, or environmental concerns.
Therefore, miners face a complex web of regulations that vary significantly across jurisdictions. Understanding these crypto mining legal frameworks is crucial for anyone considering mining operations, as regulatory compliance directly impacts profitability, operational sustainability, and investor security. This comprehensive guide examines the current state of crypto mining regulations worldwide and what miners need to know before setting up operations in 2025. We already have list of countries where there’s a cheaper mining cost, read now and high profitability.
Why governments regulate crypto mining
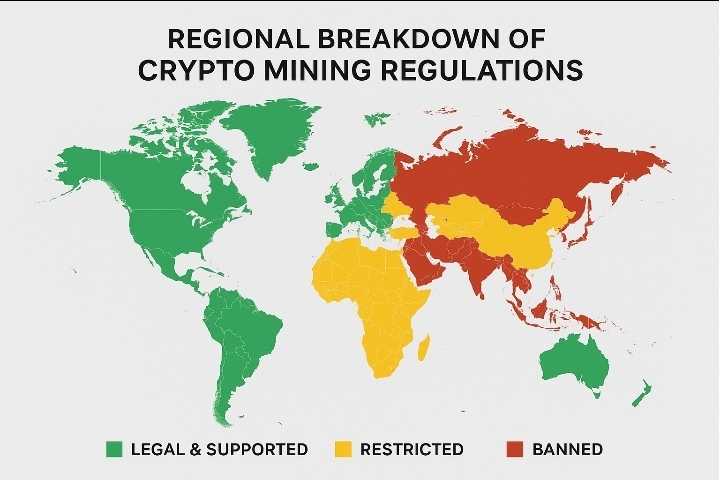
Governments worldwide have identified several key concerns that drive their regulatory approaches to cryptocurrency mining. Energy consumption and environmental impact top the list of regulatory priorities. Bitcoin mining alone consumes more electricity annually than entire countries like Argentina, prompting governments to implement strict energy usage guidelines and environmental standards.
Anti-money laundering (AML) and tax compliance represent another critical regulatory focus. Mining operations can potentially facilitate illicit financial activities if left unchecked. Governments require miners to implement robust KYC procedures and maintain detailed transaction records to prevent their operations from being exploited for money laundering or terrorist financing.
Data security and prevention of illegal computing resource usage have become increasingly important as cybercriminals target mining infrastructure. Regulators now mandate specific security protocols to protect mining facilities from unauthorized access and ensure computing resources aren’t hijacked for illegal purposes.
Key areas of regulation of crypto mining
Licensing and registration requirements form the foundation of most regulatory frameworks. Many jurisdictions now require mining operations to obtain specific licenses before commencing activities. These licenses often come with ongoing compliance obligations and regular reporting requirements.
Tax obligations for mining income vary significantly by jurisdiction but generally fall into two categories. Some countries treat mined cryptocurrency as ordinary income taxed at standard rates, while others classify it as capital gains subject to different tax treatment. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for maintaining compliance and optimizing tax efficiency.
Electricity and energy policy compliance has become increasingly stringent. Regulators often impose limits on energy consumption, require the use of renewable energy sources, or implement special tariffs for high-energy users like mining operations. Some jurisdictions have introduced carbon offset requirements for mining activities.
Hardware import and export restrictions can significantly impact mining operations. Several countries restrict the importation of mining equipment, while others impose hefty tariffs. These regulations aim to control the growth of domestic mining industries and manage their environmental impact.
Countries where crypto mining is fully legal and encouraged in 2025
These are the legal & regulatory environment of crypto mining by jurisdictions.
The United States maintains a complex regulatory environment where mining legality varies by state. Texas has emerged as a mining hub due to its deregulated energy market and pro-crypto stance. Wyoming offers favorable tax treatment and clear regulatory frameworks. Kentucky provides tax incentives for mining operations that create local jobs.
Canada continues to attract miners with its cold climate, abundant renewable energy, and clear federal regulations. The country treats mining as a business activity subject to standard tax rules. Provincial regulations vary, with Quebec implementing specific energy allocation policies for miners.
Kazakhstan has positioned itself as a global mining destination despite recent regulatory tightening. The country offers low electricity costs and has implemented a licensing regime that provides legal clarity for operators. However, energy shortages have led to temporary restrictions during peak demand periods.
The United Arab Emirates has embraced crypto mining as part of its economic diversification strategy. Dubai’s Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority provides comprehensive licensing frameworks, while free zones offer attractive incentives for mining businesses.
Countries with partial restrictions or licensing requirements
China once dominated global Bitcoin mining but implemented a complete ban in 2021. The prohibition covers all mining activities and cryptocurrency transactions, forcing miners to relocate operations to other jurisdictions. This ban significantly reshaped the global mining landscape.
Russia presents a complex regulatory environment. While mining itself is legal, using cryptocurrencies for domestic payments remains prohibited. The government has introduced licensing requirements for large-scale operations and is developing comprehensive mining regulations expected to take effect in 2025.
India maintains an ambiguous stance on mining. While not explicitly banned, the 30% tax on crypto gains and lack of clear regulations create uncertainty. Several states have restricted mining operations due to energy concerns, while others remain more permissive.
Indonesia prohibits using cryptocurrencies as payment instruments but allows mining as a commodity-producing activity. Miners must register with authorities and comply with specific technical and financial requirements.
Countries where crypto mining is banned
Bangladesh maintains a complete prohibition on all cryptocurrency activities, including mining. Violations can result in imprisonment under the country’s strict anti-money laundering laws. The ban extends to holding, trading, and mining cryptocurrencies.
Nepal similarly prohibits all cryptocurrency activities. The Nepal Rastra Bank has declared cryptocurrencies illegal, and mining operations face criminal prosecution. Authorities actively monitor electricity usage to detect illegal mining operations.
Algeria banned cryptocurrencies in 2018, declaring their use, holding, and mining illegal. The prohibition aims to protect the national currency and prevent capital flight. Penalties include fines and imprisonment for violations.
Morocco maintains a comprehensive ban on cryptocurrency activities. The Office des Changes declared all virtual currency transactions illegal, including mining operations. Banks actively monitor and report suspected cryptocurrency-related activities.
Regional Breakdown of Crypto Mining Regulations
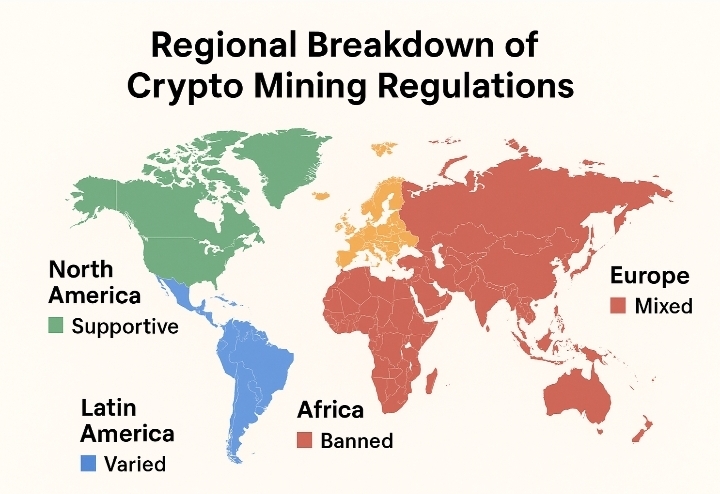
Take a closer look at how different parts of the world approach cryptocurrency mining. Understanding these regional differences helps you identify the most secure and profitable countries to invest.
Is Crypto mining Legal in North America?
The United States presents a patchwork of state regulations. Texas leads in mining-friendly policies, offering competitive electricity rates and minimal regulatory barriers. The state’s deregulated energy market allows miners to negotiate directly with power providers. New York has implemented a two-year moratorium on proof-of-work mining using non-renewable energy sources, reflecting environmental concerns. Kentucky offers tax breaks for mining operations that meet specific investment and job creation thresholds.
Canada’s approach varies by province. Quebec initially welcomed miners but later imposed moratoriums due to energy capacity concerns. The province now allocates specific energy blocks to mining operations through a selection process. Alberta and Manitoba offer more favorable conditions with abundant renewable energy and supportive regulatory frameworks. Federal regulations require mining operations to register as money service businesses if they engage in cryptocurrency exchanges.
Is Crypto Mining Megal in Europe?
The European Union’s Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation, which came into effect in 2023, establishes comprehensive rules for crypto activities. While MiCA primarily focuses on crypto assets and services, it impacts mining operations through environmental sustainability requirements. The EU is considering specific regulations targeting proof-of-work mining’s environmental impact.
Germany treats mining as a commercial activity subject to standard business regulations. Mined cryptocurrencies are considered private money, and profits are subject to income tax. The country’s high energy costs make large-scale mining less attractive despite regulatory clarity.
Sweden and Norway have become attractive mining destinations due to abundant renewable energy and cold climates. However, Sweden has proposed an EU-wide ban on proof-of-work mining, citing environmental concerns. Norway offers competitive energy prices but has faced political pressure to restrict mining operations’ energy access.
Is Crypto Mining Legal in Asia-Pacific?
China’s 2021 mining ban triggered a massive exodus of mining operations. The ban encompasses all mining activities, with authorities monitoring electricity usage to detect violations. Former mining hubs like Inner Mongolia and Xinjiang now actively prosecute illegal mining operations.
Kazakhstan absorbed many Chinese mining operations but has since tightened regulations. The country requires mining operations to obtain licenses and pay elevated electricity rates. Power shortages have led to temporary shutdowns and capacity restrictions during winter months.
Malaysia has emerged as a mining destination, though regulatory clarity remains limited. Authorities have cracked down on illegal mining operations stealing electricity while working to develop comprehensive regulations for legitimate operators.
Japan maintains clear regulations treating mining as a business activity. Mined cryptocurrencies are classified as miscellaneous income for tax purposes. The country’s high electricity costs limit large-scale mining viability despite regulatory clarity.
Is Crypto Mining Legal in Africa
Nigeria presents a complex environment where cryptocurrency banking is restricted, but mining itself isn’t explicitly prohibited. The lack of reliable electricity infrastructure poses practical challenges for mining operations. Recent government initiatives suggest potential regulatory frameworks are under development.
Kenya has shown increasing interest in cryptocurrency adoption. While specific mining regulations don’t exist, the government is developing comprehensive crypto frameworks. The country’s geothermal energy resources present opportunities for sustainable mining operations.
South Africa treats cryptocurrency mining as a legitimate business activity. The South African Revenue Service requires miners to declare income from mining activities. Energy constraints and rolling blackouts present operational challenges despite regulatory acceptance.
Is Crypto Mining Legal Latin America
El Salvador’s Bitcoin adoption extends to mining initiatives. The government operates geothermal-powered mining facilities using volcanic energy. Private mining operations benefit from clear regulatory frameworks and government support for the cryptocurrency sector.
Argentina attracts miners with subsidized electricity rates in certain provinces. However, recent economic instability and energy shortages have led to restrictions in some regions. Miners must navigate provincial regulations that vary significantly across the country.
Brazil legalized cryptocurrencies as payment methods in 2023, providing clearer frameworks for mining operations. The Central Bank oversees crypto regulations, treating mining as a legitimate business activity subject to standard tax obligations.
Taxation & Compliance for Crypto Miners
Individual miners typically face different tax treatment than commercial operations. In most jurisdictions, individuals must report mined cryptocurrencies as income at their fair market value when received. This creates tax obligations even before converting crypto to fiat currency.
Business mining operations generally benefit from more favorable tax treatment. They can deduct operational expenses including electricity, hardware depreciation, and facility costs. However, they must maintain detailed records and may face additional reporting requirements.
Reporting and record-keeping requirements
Transaction logs must capture every mining reward received, including timestamps and values. Sophisticated mining operations use specialized software to automate this process and ensure accuracy. These records prove essential during tax audits and compliance reviews.
Wallet tracking and KYC compliance have become mandatory in many jurisdictions. Miners must verify their identity with mining pools and exchanges. Some countries require miners to report wallet addresses to tax authorities, enabling transaction monitoring.
Common tax mistakes miners make
Unreported income remains the most common compliance failure. Miners sometimes assume they only owe taxes when converting crypto to fiat, but most jurisdictions tax mining rewards upon receipt. This misunderstanding can lead to significant penalties and interest charges.
Incorrect deductions often occur when miners claim personal expenses as business costs. Home miners must carefully allocate electricity and space usage between personal and mining activities. Professional tax advice proves invaluable for navigating these complexities.
Environmental & Energy Regulations
Electricity consumption limits and sustainability laws
Governments increasingly impose specific limits on mining operations’ energy consumption. Some jurisdictions cap total energy usage per facility, while others implement progressive pricing structures that penalize excessive consumption. These regulations aim to prevent mining operations from straining local power grids.
Green or renewable energy incentives for miners
Forward-thinking jurisdictions offer substantial incentives for miners using renewable energy. These include tax credits, reduced electricity rates, and streamlined permitting processes. Some countries require minimum renewable energy percentages for new mining operations.
Impact of carbon taxes and emissions reporting
Carbon pricing mechanisms significantly impact mining profitability in many jurisdictions. Miners must calculate and report their carbon footprint, paying taxes based on emissions. This has accelerated the industry’s shift toward renewable energy sources and more efficient hardware.
Future Trends in Crypto Mining Regulation
The role of AI and blockchain transparency tools
Artificial intelligence increasingly helps regulators monitor mining operations and detect non-compliance. Blockchain analytics tools enable authorities to track mining rewards and identify operations attempting to evade regulations. Miners must prepare for enhanced scrutiny through technological means.
Global cooperation on energy efficiency standards
International bodies are developing standardized efficiency metrics for mining operations. These standards may become mandatory, requiring miners to meet minimum efficiency thresholds. Early adoption of efficient practices positions miners favorably for future compliance.
Predictions for 2026-2030 regulatory direction
Experts anticipate increased harmonization of mining regulations across jurisdictions. Environmental considerations will likely drive stricter energy requirements, while tax frameworks should become more standardized. Proof-of-stake transitions may reduce regulatory pressure on energy-intensive mining.
How to Stay Compliant as a Miner
Legal due diligence checklist: Before starting operations, miners must research local and national regulations thoroughly. This includes understanding licensing requirements, tax obligations, and energy regulations. Consulting with legal professionals familiar with cryptocurrency regulations proves essential for avoiding costly mistakes.
Ongoing compliance requires regular regulatory updates and policy adjustments. Miners should establish relationships with local authorities and industry associations. Participating in regulatory consultations helps shape favorable policies while demonstrating good faith compliance efforts.
Working with compliant cloud mining services: Cloud mining offers an alternative for those seeking mining exposure without regulatory complexity. However, due diligence remains crucial when selecting providers. Verify their regulatory compliance, physical location, and track record before investing.
Using tools for tax and energy tracking: Modern mining operations require sophisticated monitoring tools. Energy management systems help optimize consumption and demonstrate regulatory compliance. Tax software specifically designed for cryptocurrency activities simplifies reporting and reduces error risks.
Conclusion
The global cryptocurrency mining regulatory landscape continues evolving rapidly. Success in this environment requires understanding and adapting to diverse regulatory frameworks across jurisdictions. Miners who prioritize compliance, environmental sustainability, and transparent operations position themselves for long-term success. As regulations mature, the industry will likely see increased standardization and clarity, benefiting legitimate operators while eliminating bad actors. Staying informed about regulatory changes and maintaining flexible operations enables miners to navigate this complex but potentially rewarding landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Bitcoin mining legal in my country? Mining legality varies significantly by jurisdiction. Research your specific country’s regulations, as laws change frequently. Consult local legal experts for definitive guidance.
Do I need a license to mine crypto? Licensing requirements depend on your location and operation scale. Many jurisdictions require licenses for commercial mining but allow small-scale personal mining without permits.
How are mining profits taxed? Most countries tax mining rewards as income when received, based on fair market value. Additional capital gains taxes may apply when selling mined cryptocurrencies. Learn more about crypto mining.
What countries ban crypto mining in 2025? China, Bangladesh, Nepal, Algeria, Morocco, and Egypt maintain comprehensive mining bans. Other countries impose partial restrictions or temporary moratoriums.
Which countries support green mining projects? Norway, Iceland, Canada, El Salvador, and Paraguay actively support renewable energy mining. These countries offer incentives for sustainable mining operations using hydroelectric, geothermal, or other renewable sources.